Keloid & Hypertrophic Scar
Keloid & Hypertrophic Scar
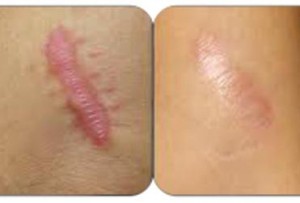
Shubham skin clinic at Pune Sinhagad road offers best advice and treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars.
Keloids are the result of an overgrowth of dense fibrous tissue that usually develops after healing of a skin injury. The tissue extends beyond the borders of the original wound, does not usually regress spontaneously, and tends to recur after excision. Keloids are harmless to general health and do not change into skin cancers.
In contrast, hypertrophic scars are characterized by erythematous, pruritic, raised fibrous lesions that typically do not expand beyond the boundaries of the initial injury and may undergo partial spontaneous resolution. Hypertrophic scars are common after thermal injuries and other injuries that involve the deep dermis.
• Most skin injury types can contribute to keloid scarring. This includes acne scars, burns, chickenpox scars, ear piercing, scratches, surgical cuts or vaccination sites.
• Keloids tend to have a genetic component, which means you are more likely to have keloids if one or both of your parents has them.
• Hypertrophic scars generally develop after thermal or traumatic injury that involves the deep layers of the dermis.
• Also mechanical tension on a wound has been identified as a leading cause for hypertrophic scar formation.
• Keloids expand in claw-like growths over normal skin.
• They have the capability to hurt with a needle-like pain or to itch without warning, although the degree of sensation varies from person to person.
• If the keloid becomes infected, it may ulcerate.
• Hypertrophic scars are thick and reddish.
• They can result in pain or itchiness.
• They do not spread outside the borders of the original wound. They can however keep thickening for nearly 6 months.
• Hypertrophic scars tend to become better after one to two years. Patients may however feel distressed due to the itchiness or their appearance.
• In case the scars form next to a joint, then it can limit the range of motion.
• Avoid scratching
• Avoid surgical removal because it may increase after removal.
• Seek proper advice and treatment from skin doctor.
